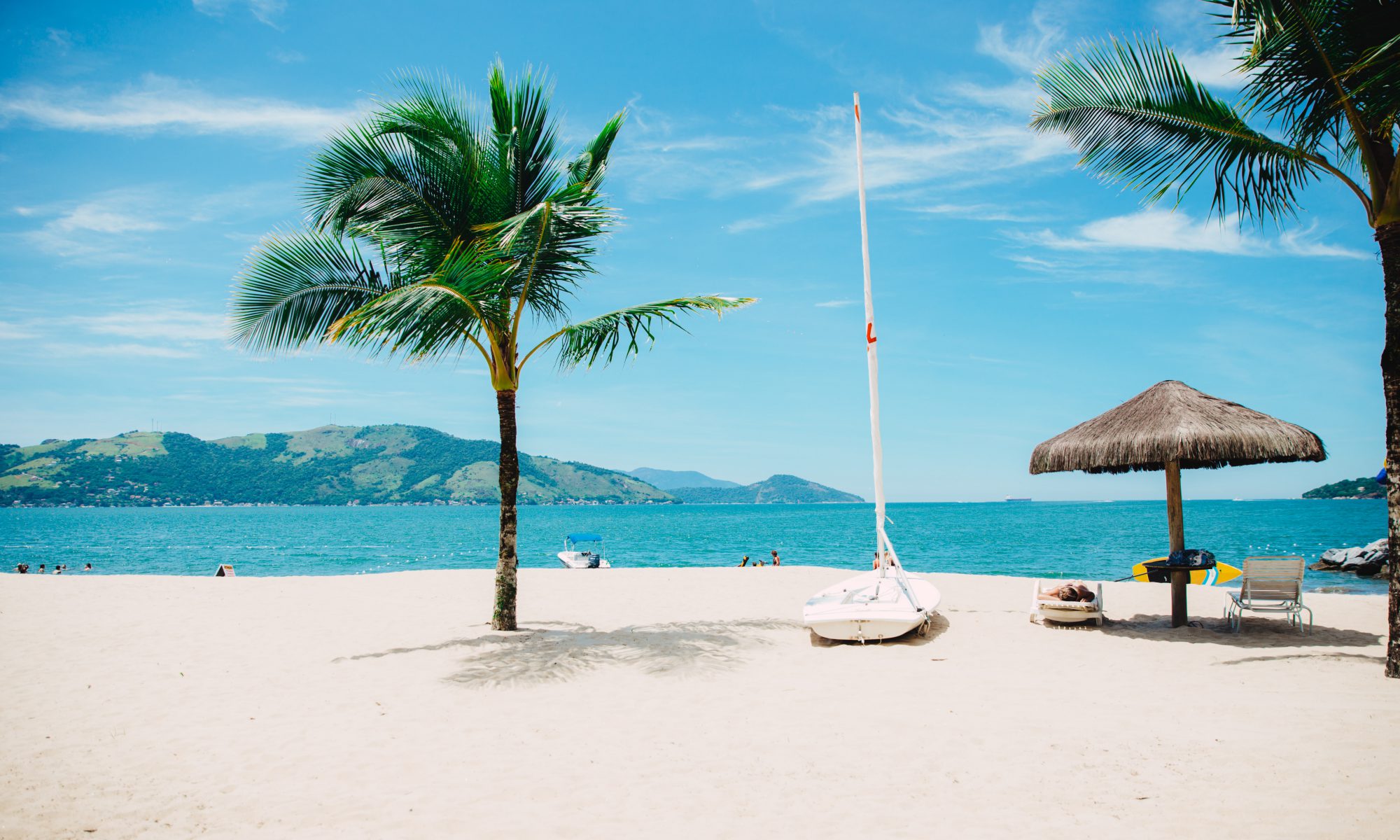
Car with passengers in the front and rear, sun protection for the rear side window Sun protection in the car
Anyone who spends time outdoors knows that they need to protect themselves from the sun. But what about in the car? Do car windows protect against UV radiation?
You are well protected from UV-B radiation in your car. It is blocked by all windows. The windshield also protects against UV-A radiation. But it’s different with the side windows: UV-A radiation can pass through them to a greater or lesser extent. This means that even with the windows closed, UV protection in the car is recommended in some situations.
When is UV protection important in the car?
On spring or sunny summer days, protection against excessive UVA radiation is recommended during long car journeys with the windows closed, when the sun shines directly on a person through the window for a long time. This is especially true for children, as their skin is extremely sensitive to UV radiation.
Protective measures
Measures against heat in the car, such as towels hung in the windows, window blinds, or sun visors, also offer protection against UV-A radiation when the windows are closed. However, such items are unsuitable for the driver’s 180-degree field of vision. Transparent UV protection films are ideal for this purpose, as they can effectively reduce UV radiation entering the interior of the car. Tinted UV protection films can also be used in the rear of the car.